The wine production process is long and complex and it is important to properly filter the wine for sanitary and hygienic reasons, to ensure a quality product. This filtration must be carried out effectively but no aggressively, in order to eliminate the impurities and microorganisms of this exquisite drink. The filtration of the wine makes it possible to preserve the organoleptic properties of each varietal, without any resulting alterations of color, brightness or gustatory nuances.
What is wine filtration?
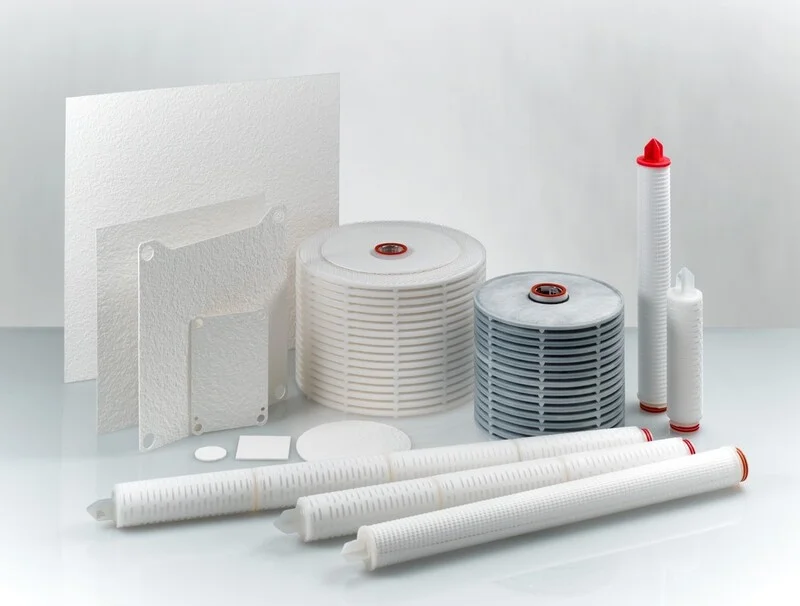
Wine filtration basically consists of the separation of suspended solid particles and grape impurities (bacteria, yeasts, bitartrate crystals, traces of raw materials, etc.). This ensures a product with the property microbiological stability and sterilization necessary to be bottled for sale on the market.
Types of filtrations
There are five different ways to carry out the filtration of the wine:
- Earth filtration. A layer of filtering soil, usually diatomaceous earth or pearlite, is used to retain or absorb the wine impurities.
- Plate filtration. Cellulose plates with different degrees of porosity are used as the filter material.
- Membrane filtration. Carried out before bottling to ensure stabilization, using a membrane with smaller pores than the particles to be filtered out.
- Filter by centrifuge. Used to purify, concentrate, desalinate and filter biological samples in the volume range of 2 to 15 ml.
- Tangential filters. Used to filter sugary solutions, concentrates and aromas.
How is wine filtered? Steps to follow
There are three basic steps to filtration, resulting in an acceleration and optimisation of the natural wine purification processes, thus achieving a purified beverage that is pleasant for the senses.
Prefiltration
The purpose of this initial phase is to remove and retain the most solid larger particles through a mechanical filtration process. It is not always necessary to perform pre-filtration. Everything depends on the type of filtration to be executed. In any case, it is recommended to increase the use of cold tartaric stabilization if using this method.
For this phase, diatom filters are usually used, which have a pre-layer in depth and are formed with diatomaceous earth or perlite with different permeabilities. Another alternative is tangential filters, which have the advantage of minimizing the loss of coloring and dry extract matter. It is also possible to complement this first filtration with centrifugal separation equipment to improve results.
Refining filtration
This second stage consists of passing the wine through refrigeration equipment to eliminate the microcrystals that could remain in suspension, as well as protecting the final membranes from sterilizing filtration. As in the previous step, diatom or tangential filtration filters may be used. This is a finer filtration, however, where it would be better to use filtration media such as the plate filter to avoid possibly stripping the wine.
Sterilizing filtration
The third and final phase is carried out before bottling in order to ensure stabilization and sterilization of the final product. Microns can be used for this stage (0.65 for yeast removal and 0.45 for bacteria). The use of one kind of filter or another depends on the type of wine and its level of quality, but whatever the choice, it is very important that the chosen sterilizing membrane is high-quality and resistant. Failure to do so may result in breakage or some sort of incompatibility with the chosen cleaning product.
Wine filtration is a complex process with various factors and multiple variables that come into play. For optimal filtering, it is essential to have sufficient knowledge, or good advice. The only way it is possible is to make the right choices in regard to:
- The filtration technology used.
- The types of filters.
- The size and sequence of the whole process.
Wine filtration must be considered as a whole process, where each stage influences the following. Thus, it is necessary to treat all phases correctly, with the appropriate sequencing, since otherwise, operational problems may occur and the final result will not come out as expected
The data obtained in the laboratory, together with knowledge of the intended final market, as well as proper maintenance of the various elements and machinery used during filtration, are the core variables to monitor to ensure proper wine filtration and achieve the highest levels of food safety and quality.
Agrovin, more than 30 years of experience in wine filtration. Contact us for more information.